The crossbridge interactions between these myofilaments drive muscle contraction and the degree of. To account for the linear relationship observed between the force generated by a smooth muscle and the muscle length at the plateau of an isotonic contraction a model of contractile unit is proposed.

Smooth Muscle Anatomy And Physiology I
They are attached to dense bodies which in turn are anchored to.

. In the walls of large arteries and attached to the hair of the skin are multi-unit fibers. Creatine phosphate functions in the muscle cell by A forming a temporary chemical compound with myosin. Details of the filament organization however are still poorly understood.
Question 6 Smooth muscle tissue A. The thin filaments in a smooth muscle cell are attached to dense bodies structures distributed throughout the sarcoplasm in a network of intermediate filaments composed of the protein desmin. View full document See Page 1.
This type of smooth muscle is observed in the large airways to the lungs in the large arteries the arrector pili muscles associated with hair follicles and the internal eye muscles which regulate light entry and lens shape. Has sarcomeres organized around dense bodies B. Has thin filaments attached to dense bodies and to the plasma membrane C.
For thin-section electron microscopy we used the isolated dense bodies with attached filaments. Several models of contractile filament architecture are discussed here. The thin filaments in a smooth.
In smooth muscle cells thin filaments are attached to _____-use aerobic respiration-red-good for endurance-high concentration of myoglobin. Actin and myosin form continuous chains within the smooth muscle cell which are anchored at the dense bodies. A dense body is analogous to the Z-discs of skeletal and cardiac muscle fibers and is fastened to the sarcolemma.
Thick and thin filaments are diagonal from side to side within smooth muscle cell in elongated diamond lattice rather than parallel lattice shortens and so does cell bulging between the points where thin filaments are attached to inner surface of the plasma membrane. Smooth muscle fibers are cigar shaped cells that range in size from 20µm in the walls of the. In vimentin-deficient smooth muscle tissues force development in response to contractile stimulation is attenuated.
The actin containing tropomyosin and troponin decorated thin filaments form one of the crucial components of the contractile apparatus in muscles. Produces much shorter contractions than skeletal muscle fibers. In smooth muscle the thin filaments are attached to _____ that will draw the cell inward during contraction.
A thick filaments B Z lines C dense bodies D myosin. The model consists of 2. Smooth muscle cells of the muscle bundles are attached to each other by desmosome-like junctions and by fusion of the basal laminae.
Actin filaments appeared to be inserted into both ends poles of individual oblong dense bodies in such a way that arrowheads with HMM S-1 pointed away from the dense body. First vimentin filaments connect with the membrane at desmosomes that are complex intercellular junctions specialized to provide strong but dynamic cell-cell adhesion in various cell types and tissues including smooth muscle 60. 10 nm filaments were attached laterally to the dense body in a side-to-side fashion.
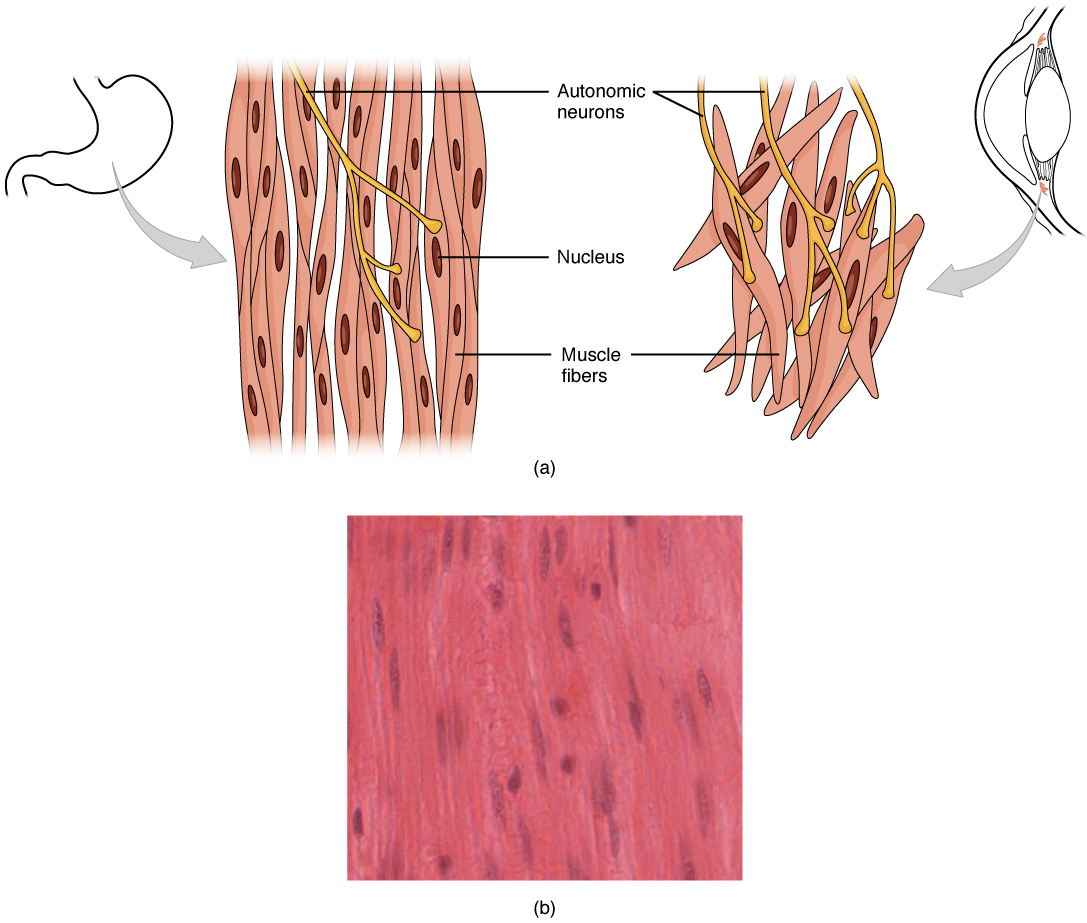
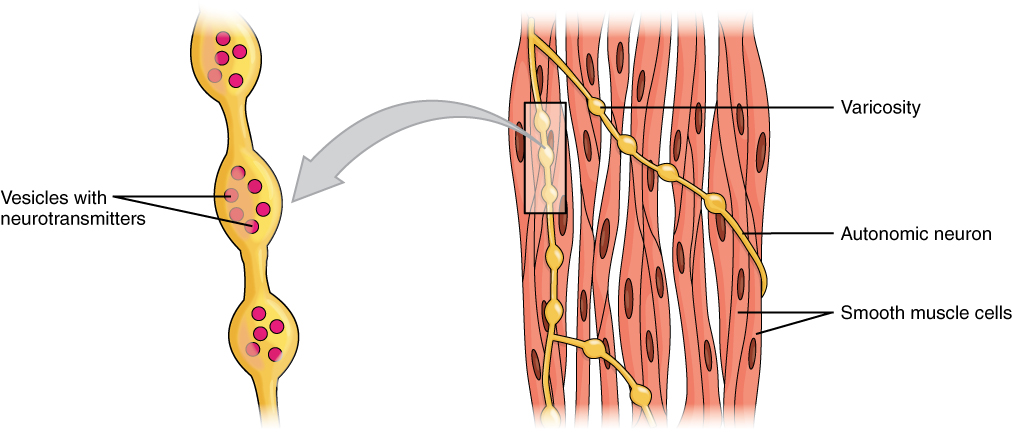
In the single unit smooth muscle the fibers are connected. Figure 1071 Smooth Muscle Tissue. The intermediate and thin filaments formed by the actin and myosin chains can then stretch to dense bodies located on adjacent smooth muscle cells forming a mesh-like network encircling a large number of smooth muscle cells.
Question 6 Smooth muscle tissue A. Has sarcomeres organized around dense bodies B. The thin filaments are organized into densely packed lattices interdigitated with myosin-based thick filaments.
The myosin proteins are organized differently than in skeletal or cardiac muscle cells and smooth muscle cells have more cross-bridges per thick filament. Smooth muscle tissue is found around organs in the digestive respiratory. Thin filaments of a smooth muscle fibre are anchored since no sarcomere or Z lines.
The ____ discs that anchor the sarcomere on either end in skeletal muscle are absent from smooth muscle cells. Although they do not have striations and sarcomeres smooth muscle fibers do have actin and myosin contractile proteins and thick and thin filaments. What part of myosin molecule does ATP bind to-around blood vessels-in the wall of.
The cytoplasm of the muscle cells is characterized by conspicuous thick filaments and abundant thin and intermediate filaments. These thin filaments are anchored by dense bodies. Thin filaments contain actin.
In smooth muscle thin filaments are attached to a Z lines b troponin c dense Course Hero In smooth muscle thin filaments are attached to a z School Health Services Academy Course Title BIO 301 Uploaded By ElderWillpower6871 Pages 35 This preview shows page 33 - 35 out of 35 pages. Do not have thick filaments D. At maximal contraction of a muscle fiber the thin.
The _____ discs that anchor the sarcomere on either end in skeletal muscle are absent from smooth muscle cells. In smooth muscle cells thin filaments are attached to what.
Smooth Muscle Anatomy And Physiology

0 Comments